Drag Conveyor Horsepower Calculation
The KWS Dragon-Flite conveyor is an efficient, high performance alternative to conventional means of material handling. Because the material is moved En-Masse, horsepower requirements can be as much as half of that of alternative means of conveyance.
The Horsepower (HP) requirements of a Dragon-Flite conveyor can be calculated as the sum of the three contributing factors to the HP requirements. The total HP requirement is the sum of the HP to move the chain/flights and sprockets called the "Empty HP" + the HP to move the material in the conveyor called the "Live HP" + the HP to lift the material in an inclined situation called the "Lift HP".
Empty HP
The Empty Horsepower is the power required to overcome the friction in the power transmission system, chain/sprockets, and the flights dragging on the bottom of the trough. Empty HP can be calculated using the following formula.
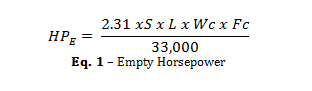
HPE = Empty Horsepower Requirement
Wc = Weight per foot of Chain and Flight (Lb/ft)
L = Length of the Conveyor (ft)
S = Speed of the Chain (ft/min)
Fc = Friction Factor of the Flights on the Bottom Housing
Note:
Frictional factor used in the above formula vary depending on the specific applications and products being conveyed. Testing may be required to determine the exact values to be used.
Live HP
The Live Horsepower is the power required to overcome the friction of the material sliding along the bottom of the housing over the length of the conveyor. Live HP can be calculated using the following formula.
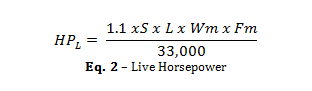
HPL = Live Horsepower Requirement
Wm = Weight per foot of Material Being Conveyed (Lb/ft)
L = Length of the Conveyor (ft)
S = Speed of the Chain (ft/min)
Fm = Friction Factor of the Material on the Bottom Housing
Note:
Frictional factor used in the above formula vary depending on the specific applications and products being conveyed. Testing may be required to determine the exact values to be used.
Lift HP
The Lift Horsepower is the power required to lift the material the required height of an inclined or bent leg conveyor. Lift HP can be calculated using the following formula.
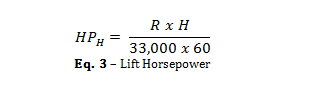
HPH = Lift Horsepower Requirement
R = Rate of Material Being Conveyed (Lb/hr)
H = Vertical Height the Material is to be Conveyed (ft)
Total HP
Using the Empty HP, Live HP, and Lift HP, the total Horsepower required to convey the material can be calculated using the following formula.
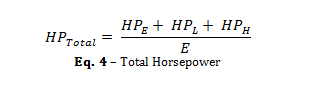
HPTotal = Total System Horsepower Requirement
HPE = Empty Horsepower Requirement
HPL = Live Horsepower Requirement
HPH = Lift Horsepower Requirement
E = Drive Efficiency
Chain Pull
Although a preliminary chain selection is required to calculate the Total HP, the actual maximum design chain pull is required in order to accurately select the appropriate chain for the conveying application. The design chain pull is calculated using the actual drive and motor selected and doing so will ensure the chain does not fail under upset conditions. Additional factors for design chain pull include the Speed Factor and Service Conditions. The design chain pull can be calculated using the following formula.
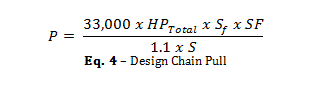
P = Design Chain Pull (LB)
HPTotal = Total System Horsepower Requirement (HP)
S = Speed of the Chain (ft/min)
Sf = Speed Factor (Table 1)
SF = Product of Service Factors (Table 2)
| Number of Teeth |
Conveyor Speed (FPM) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 25 | 50 | 75 | 100 | 125 | 150 | 175 | 200 | |
| 6 | 0.917 | 1.09 | 1.37 | 1.66 | 2 | 2.4 | 2.97 | 3.57 | 4.41 |
| 7 | 0.855 | 0.971 | 1.13 | 1.27 | 1.44 | 1.61 | 1.31 | 2.04 | 2.29 |
| 8 | 0.813 | 0.909 | 1.04 | 1.16 | 1.26 | 1.37 | 1.49 | 1.63 | 1.76 |
| 9 | 0.794 | 0.87 | 0.98 | 1.07 | 1.17 | 1.26 | 1.36 | 1.45 | 1.55 |
| 10 | 0.775 | 0.84 | 0.943 | 1.02 | 1.09 | 1.16 | 1.24 | 1.31 | 1.37 |
| 11 | 0.758 | 0.82 | 0.901 | 0.971 | 1.03 | 1.09 | 1.15 | 1.22 | 1.28 |
| 12 | 0.741 | 0.787 | 0.862 | 0.926 | 0.99 | 1.05 | 1.1 | 1.16 | 1.21 |
| 14 | 0.735 | 0.769 | 0.833 | 0.885 | 0.935 | 0.98 | 1.02 | 1.07 | 1.11 |
| 16 | 0.725 | 0.763 | 0.813 | 0.855 | 0.893 | 0.935 | 0.971 | 1.01 | 1.05 |
Table 1 – Speed Factor (Sf)
| Vs | Vl | Vo | Vt | Factor |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Frequency of Shocks | Character of Loading | Operating Conditions | Daily Operating Times | |
| Infrequent | Uniform or Steady | Clean and Moderate Temperature | 8-10 Hr | 1.0 |
| Frequent | Moderate | Dusty | 24 Hr | 1.2 |
| Unprotected or Harsh | 1.4 | |||
| Heavy | 1.5 |
Table 2 – Service Factors (SF)
The above information and formulas are a conservative approach to drag conveyor horsepower and chain pull design. More detailed information can be found in the Standard Handbook of Chains by the American Chain Association.






